Unit 4: Highmark Member Information
1.4 Identifying Highmark Members
1.4 Member Identification Cards
1.4 Verifying Eligibility and Benefits
1.4 Confidentiality of Member Information
1.4 Advising Members of Treatment Options
1.4 Member Access to Physicians and Facilities
1.4 Communication Aids and Services
1.4 Administrative Fee Collection Guidelines
Member
A member is an individual who is enrolled in a health plan and who meets the eligibility requirements of the program.
Subscriber
A subscriber is a member whose employment or other status, except for family dependency, is the basis for eligibility for enrollment in a program.
Dependent
A dependent is any member of a subscriber’s family who meets the applicable eligibility requirements and is enrolled in a program.
Managed Care Plans
Managed care plans are delivered through a provider network. Under some plans, members may visit providers in or out-of-network; however, the highest level of benefits are paid for visits to in-network providers.
Managed care plans include:
- Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs);
- Point of Service (POS);
- Open Access;
- Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs); and
- Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs).
Indemnity Plans
Traditional indemnity plans are sometimes referred to as fee-for-service plans in that they pay a set amount per health care service performed. It gives members the widest choice of physicians and services through participating providers. Generally, these plans are subject to a deductible and coinsurance.
A Highmark member can be easily identified by the information on his or her identification (ID) card. Always ask to see the ID card upon the patient’s first visit. On subsequent visits, ask the patient if he or she has had a change in health insurance. A patient’s insurance information can change at any time and incorrect information can result in delayed claim payment. Although the ID card provides enrollment information for a Highmark member, it is recommended that you always confirm eligibility for the date of service through Availity, Highmark’s internet-based inquiry system, or by performing an electronic HIPAA 270 Eligibility/Benefit Inquiry transaction.
Member ID Cards
All Highmark members receive an identification card so you can easily identify them and have essential information to help you understand their coverage. The identification cards may have slight variations depending upon the type of program and the location of the Blue Plan through which members are enrolled. There may also be some small variances on cards of each employer group. Practices with the fewest claim submission errors generally require the member to show the current ID card with each visit and verify eligibility on every visit/service. This is why it is important to check the member’s identification card prior to each visit or service you provide.
Generally, the identification card includes the following information:
- Subscriber’s name;
- Dependent’s name, if applicable;
- Member’s Unique Member Identifier (UMI), or “Member ID,” which includes a 3-character prefix and a 12-digit identification number;
- Group number – a series of alphabetical and numeric characters assigned to employment groups, professional associations, and direct payment programs;
- Plan Code – three digits that identify the Blue Plan through which the member is enrolled;
- Type of agreement – a brief description of the type of agreements and coverage of the member (not all identification cards have this information); and
- BlueCard® – all BlueCard members can be identified by a 3-character prefix preceding the member identification number on their identification card. Always report the 3-character prefix from any ID card.
Members may have more than one identification card if they are covered under more than one plan. Please verify the correct prefix and identification number for reporting services.
Prefix
The 3-character prefix at the beginning of the member’s identification number is the key element used to identify and correctly route claims. The Blue Cross Blue Shield Association (BCBSA) issues “alphanumeric prefixes” to Blue Plans.
Occasionally, Highmark will assign new alphanumeric prefixes when new groups are created. Please be aware that you may be seeing local Highmark members with valid alphanumeric prefixes on their Member ID cards. Since existing prefixes will not change, you will also continue to see the familiar “alpha prefixes.”
Please see the manual’s Chapter 2 Unit 6: The BlueCard Program, section titled “How to Identify BlueCard Members,” for more information on the BCBSA 3-character prefixes that can be either three alpha characters or a combination of alpha and numeric characters.
Important! Medicare Advantage members retain their Medicare cards even after they begin coverage under Highmark Medicare Advantage products. You should always ask Medicare-eligible patients if they have joined a Highmark Medicare Advantage plan and, if they have, request their Highmark Medicare Advantage ID card. If a new Highmark member comes to the office and has not yet received an identification card, they may present an enrollment form or, for Medicare Advantage, a letter of confirmation in lieu of an ID card.
Identification cards are issued to all Highmark subscribers and their dependents. The ID cards feature a simplified format with key information regarding benefits and eligibility. Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association (BCBSA) regulations require subscriber identification cards of all Blue Plans to follow the same format. Highmark’s member identification cards satisfy BCBSA requirements.
The BCBSA required design features of the identification card include:
- Background color: The background of the card must be white only.
- Easily identifiable standardized “zones” for display of information: The front of the card features eight easily identifiable zones, while the back is divided into five zones. Horizontal black lines mark divisions among zones.
- Blue Plan name and logo: The Highmark company name and logo appears on the left side of the top section of the ID card.
- Member name and Member ID: The member name followed by the member identification number will always appear below the Highmark logo.
- Name of the product under which the member has coverage: The member’s Highmark product is displayed on the right side of the top section of the ID card. An employer group name may also appear here.
- Blue Cross Blue Shield Association’s “suitcase” logo: The suitcase logo, identifying BlueCard participation, appears in the lower right corner.
- Prescription Drug Program group number: This number appears on the front of the card, in the third zone on the left, along with the member’s medical Group Number and the Blue Cross/Blue Shield Plan Area Code.
- PCP: The PCP name will appear if a valid PCP has been chosen.
- ID cards for dependents: Both the subscriber and dependent information appear on a dependent’s ID card. Subscriber information is on the left side of the front of the card while dependent information is on the right.
- Copays: Copays - such as PCP, Office Visit, Specialist Visit, Emergency Room - may appear if applicable.
- Coverage effective date information on individual products (“Direct Pay”): This information is no longer provided on the ID card for members with employer-sponsored coverage.
- Back of card: The applicable Blue Cross and/or Blue Shield symbols will be at the top. The internet address of the Blue Plan must appear in bold-face type on the right side of the top section of the ID card, with all relevant telephone numbers in bold-face type below it.
Front of a Standard Member ID Card
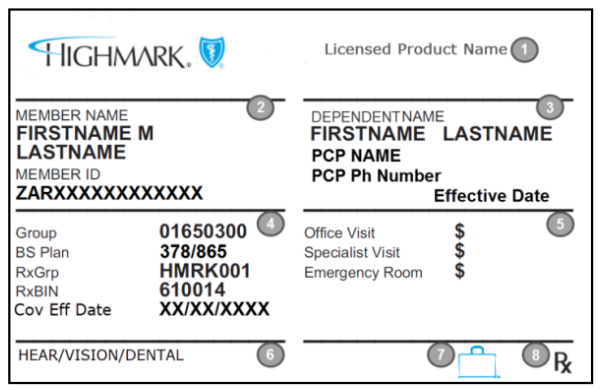
The Highmark company name/logo will always appear on the left side of the top section of the front of the ID card. Other areas will be populated as follows (numbers correspond to numbered areas on the sample ID card above):
- Licensed Product Name: The product name, such as PPO Blue or Community Blue PPO, will appear here and will help you determine which network rules to follow.
- Member Identification Information:
- The Member Name is the individual, or “subscriber,” under whose name the coverage was established.
- The member’s identification number, or Member ID,” includes the 3-character prefix that varies by employer group or account (not applicable to Medicare Advantage products).
- Dependent and PCP Information (if applicable):
- Both the subscriber and dependent information will appear on a dependent’s ID card, with the dependent’s name in this section on the right. Always verify that you have the card that corresponds with your patient and not that of another family member/dependent.
- The PCP’s name will appear here if a valid PCP is chosen.
- Medical and Pharmacy Claims Processing Information:
- The group number identifies the member’s medical group.
- The 3-digit Plan Codes identify the corresponding Blue Plan.
- The RxGrp/RxBIN numbers identify the applicable prescription coverage information.
- Member Cost Sharing:
- PCP, specialist office, office visit, and/or emergency room copayments may be listed. Specialist copays may not be the same for behavioral health care services, therapies, or diagnostic services; those copayments may be found via Availity or by calling the phone number on the back of the ID card.
- Pharmacy copayments are not listed. Participating pharmacies can verify copayment amounts online.
- Additional Coverage Information: Other coverage information may be indicated here, such as hearing, vision, and/or dental.
- Suitcase Logo: Indicates a member of the BlueCard® program. For more information about BlueCard, please refer to Chapter 2 Unit 6: The BlueCard Program of the Highmark Provider Manual.
- Rx Logo: This will be on the ID card whenever a Highmark prescription drug program is included.
Back of the Member ID Card
The back of the member’s identification card contains information mainly for the member’s use. The information may differ based on the product and may include, but is not limited to, the information outlined below.
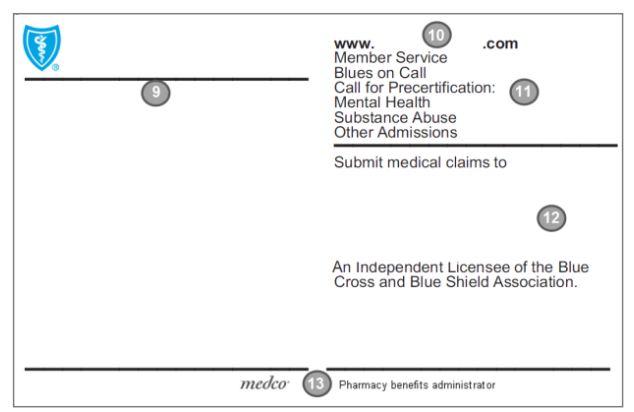
- Plan Specific Information: Benefit and administrative information specific to Highmark and/or the member’s coverage such as advising the member how to receive the highest level of benefits by obtaining care from an in-network provider.
- Plan Website: Identifies the Blue Plan’s website address to access Plan information online.
- Plan Contact Information:
- Blues On Call phone number to call for health education and support services.
- Member Service phone number for members to call Highmark with questions about benefits, claims, etc.
- Additional telephone numbers for members to receive assistance in obtaining admission to non-participating hospitals, facilities, mental health, and substance abuse treatment programs, etc.
- Claim Submission Information and Independent Licensee Disclosure: Lists addresses for member submitted claims. The “tag line” identifying Highmark as an independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association will be found here.
- Pharmacy Benefits Administrator and Logo: The name and logo of the pharmacy benefits administrator may appear here, if applicable.
Digital Member ID Cards
Highmark members can access digital versions of their ID cards through the member portal. These digital cards are equivalent to physical cards and provide real-time eligibility and benefits information. For proof of coverage, members may present these cards on their phones. Members also have the option to download and share them via email or text. For provider convenience, offices can print or save digital ID cards as PDFs in Availity. Digital ID cards should always be honored for appointments or services.
Examples of Highmark Member ID Cards
The Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association (BCBSA) regulations require that all subscriber identification cards be in the requisite format. Therefore, you should accept only those cards in the design format described within this unit. Click on the link for your region to view samples of Highmark’s ID cards:
- Highmark Blue Cross Blue Shield (DE) ID Card Samples
- Highmark Blue Cross Blue Shield (WNY) ID Card Samples
- Highmark Blue Cross Blue Shield (WPA/NEPA) ID Card Samples
- Highmark Blue Cross Blue Shield (WV) ID Card Samples
- Highmark Blue Shield (CPA/SEPA) ID Card Samples
- Highmark Blue Shield (NENY) ID Card Samples
It is the responsibility of the provider to verify that the member’s benefit plan provides the appropriate benefits for the anticipated date of service prior to rendering service. Highmark recommends that providers confirm a member’s eligibility on the anticipated date of service or one business day prior to the anticipated date of service. You can verify a Highmark member’s coverage by using Availity® or performing an electronic HIPAA 270 Eligibility/Benefit Inquiry transaction, or by calling the Provider Service Center.
HIPAA 270 Eligibility and Benefit Inquiry Transaction
Highmark’s Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) transaction system supports transactions adopted under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA). Eligibility and benefits for Highmark members can be verified by performing an electronic HIPAA 270 Eligibility/Benefit Inquiry transaction. For more information on electronic connectivity with Highmark, click the applicable link below:
You may contact the EDI Operations support line at 800-992-0246.
Provider Service Center
For those providers who are not Availity-enabled or without electronic capabilities, Provider Service Center representatives are available to provide information about Highmark member eligibility and benefits. For Provider Service Center contact information in your region, see the manual’s Chapter 1, Unit 2: Online Resources and Contact Information or go to the Contact Us page.
Verifying Eligibility For Bluecard® Members
To verify eligibility for BlueCard® members, please use Availity or call 800-676-BLUE. For additional information about BlueCard, please see the manual’s Chapter 2 Unit 6: The BlueCard Program.
Additional information is also available in the BlueCard Information Center on the Provider Resource Center – select Provider Network, then Inter-Plan Programs from the main menu at the top of the page.
Limitations
It is a member’s responsibility to timely notify his/her employer of eligibility changes (e.g., divorce, loss of student status) and the group’s responsibility to notify Highmark timely of such changes. Highmark cannot accurately verify eligibility if the member or group does not timely notify us of eligibility changes.
On rare occasions, an insured group may be terminated retroactively by Highmark for non-payment of premiums (groups are allowed at least a 30 day grace period for payment of premiums). Similarly, a self-funded group may be terminated retroactively for non-payment of claims or administrative expenses. In both cases, eligibility of the members is terminated as of the date the group is terminated. In all cases, a provider may bill the patient directly for the cost of any services provided after the effective date of termination. Also, Highmark may terminate an individual member retroactive to the last day of the month the individual was eligible.
Health Care Reform (HCR)
The Patient Protection & Affordable Care Act (PPACA) is a federal law, enacted on March 23, 2010, that makes health insurance coverage available to all Americans. The provisions in the new law are collectively referred to as Health Care Reform (HCR).
One of the many provisions of the law requires that all health benefit plans provide coverage for dependents on their parents’ policy up to age 26 years. All health plans (individual and group health insurance, including self-funded plans) that cover children as dependents must continue to make that coverage available until the adult dependent reaches age 26 regardless of whether the adult dependent is married or a student.
ACT 4 of 2009: Health Insurance Coverage for Adult Children
Pennsylvania Act 4 of 2009, Health Insurance Coverage for Adult Children, expands health insurance coverage for children of insured parents. It allows adults up to age thirty (30), under certain conditions, to remain covered by their parents’ health insurance. It is a state mandate that gives employer groups the option to extend health insurance coverage to the children of their employees up to and including age twenty-nine (29) years.
While Act 4 provides an opportunity for many young adults to obtain health insurance, it does not require that employers offer coverage to adult children of their employees. Act 4 does require licensed insurers to offer employer groups this option at the insured employee’s expense.
Verifying Dependent Eligibility
The changes in dependent eligibility will be relatively seamless for providers. Adult dependents with coverage under their parents’ agreement will have a Highmark ID card providing the applicable member identification number.
As always, request the member’s ID card on each visit, and then verify coverage and benefits through the Availity Eligibility and Benefits function. Availity is the preferred tool for inquiring about Highmark member information. Availity-enabled providers are expected to use this tool for all routine eligibility, benefit, and claim status inquiries. For those providers not Availity-enabled, eligibility can be verified by submitting a HIPAA 270 Eligibility/Benefit Inquiry transaction or by calling the Provider Service Center.
Please see Chapter 1, Unit 2: Online Resources and Contact Information for more information on contacting the Provider Service Center in your region.
Confidentiality Policy
In accordance with the highest standards of professionalism, and as a requirement of all provider contracts, providers are obligated to protect the personal health information of the Highmark members they treat from unauthorized or inappropriate use.
Member Rights and Responsibilities
Highmark treats members in a manner that respects their rights and will clearly communicate Highmark’s expectations of our member responsibilities. Please see Chapter 1 Unit 5: Member Rights and Responsibilities to review our members’ rights and responsibilities.
Normal Business Operation
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability (HIPAA) Privacy Rule generally allows Highmark to use and disclose members’ protected health information (PHI) for treatment, payment, and health care operations. Examples include:
- Claims management
- Certain types of routine audits by Highmark’s group customers
- Coordination of care
- Quality assessment and measurement
- Case management
- Utilization review
- Performance measurement
- Customer service
- Credentialing
- Medical review
- Underwriting
Release of Information for Non-Routine Use
If member information is needed for reasons other than those listed above, Highmark must generally obtain the member’s consent via an Authorization for Disclosure form.
If a member is unable to give informed consent, Highmark has a process to obtain this permission through a parent or legal guardian signature, signature by next of kin, or attorney-in-fact. The member has the right to limit the purposes for which the information can be used and all concerned are obligated to respect that expressed limitation.
Internal and External Controls
Members of Highmark products benefit from the many safeguards Highmark has in place to protect the use of data it maintains. This includes comprehensive privacy and security training of members of Highmark’s workforce; requiring Highmark employees to sign statements in which they agree to protect members’ confidentiality; using computer passwords to limit access to members’ PHI; and including confidentiality language in our contracts with doctors, hospitals, vendors, and other health care providers.
Providers’ Responsibility to Protect PHI
Members must not be interviewed about medical, financial, or other private matters within the hearing range of other patients. Practitioners must have procedures in place for informed consent and the storage and protection of medical records. Highmark will verify that these policies/procedures are in place as part of the onsite review process, when applicable.
IMPORTANT: Part 2 Substance Use Disorder Providers Must Obtain Patient Consent Before Claim Submission
If a provider, whether in-network or out of network, treats or diagnoses patients for Substance Use Disorders or refers patients for treatment of Substance Use Disorders and is subject to the Confidentiality of Substance Use Disorder Patient Records Rule (42 C.F.R. Part 2) as a Part 2 Program, payment of any claim a provider submits for such services is contingent upon compliance with the following requirements. “Part 2 Program,” “Part 2 Records,” and “Substance Use Disorder” shall have the meanings provided in 42 C.F.R. § 2.11.
Provider shall comply with the following requirements with respect to any claim or other communication it submits to Highmark that contains Part 2 Records:
- A provider is prohibited by law from disclosing Part 2 Records, including but not limited to submitting claims to the health plan, without obtaining patient consent.
- By submitting any claim (or other record) that contains Part 2 Records, the provider certifies that patient consent has been obtained and includes all required elements required by law.
- Providers may use this Authorization of Disclosure form or their own form that is compliant with Part 2.
Physicians and all other Highmark participating providers are also bound by their contracts to comply with all state and federal laws protecting the privacy of members’ personal health information.
Processes to Protect Confidentiality of Provider and Member Information and Medical Records
- Provider Profiling Data and Member information will be held confidential and will be limited to the Clinical Services staff involved in the initiatives.
- Requests for provider/member information must be in writing.
- Requests for provider information from outside sources, which may include, but not limited to, the New York State Department of Health and/or attorneys require a subpoena and accompanying court order be submitted to the Health Plan Legal Department. For release of drug and alcohol treatment records covered by 42 CFR Part 2, a subpoena by itself is insufficient. The subpoena must be accompanied by a court order, or the consent of the member, unless specific exceptions exist (for example, an emergency as defined in the regulations).
- Documents are retained and stored securely in accordance with the Records Management Compliance Program – Government Markets Policy: GUID- 5089764.
- Any documents prepared for external review must be approved by the Manager, and in some cases the Law Department.
- A copy of the request is filed in the provider’s file.
- Obsolete records (electronic or hard copy) are destroyed or discarded in a controlled, consistent, and confidential manner in accordance with the Enterprise Risk and Governance Records Management Compliance Program policy.
- For data pertaining to alcohol/substance use, during an audit, if the audit or evaluation is conducted by a health oversight agency, (e.g., NYS Department of Health is on site for contract survey purposes), patient-identifying information may be disclosed so long as the health oversight agency makes the written commitments required by 42 CFR §2.53 and the disclosure meets the requirements in 45 CFR §164.512.
- Alcohol/Substance use: The records of patients treated for alcohol or drug use are protected from disclosure by both federal and state statutes. The federal restrictions on disclosure of such information are set forth at 42 U.S.C. §290dd-2 and in Regulations at 42 C.F.R. Part 2. These provisions generally prohibit the disclosure of records of the identity, diagnosis, prognosis, or treatment of any patient, which is maintained in connection with any alcohol or drug abuse program, conducted, regulated, or assisted by a federal department or agency, without the prior written consent of the patient or under very limited exceptions.
- If the health oversight agency copies or removes patient records, it must agree in writing to abide by the requirements of 42 CFR §2.53(b).
- Article 27-F of the Public Health Law prohibits the disclosure of information concerning whether an individual has been tested for or has contracted HIV/ AIDS and any information which identifies or reasonably could identify an individual as having one or more of such conditions. Section 33.13 of New York’s Mental Hygiene Law prohibits the disclosure of data relating to a person’s mental health. Any disclosure of information governed by these laws will be pre-approved by the Legal Department.
Provider Breach Notification Obligations
All personally identifiable information (“PII”) about Highmark’s Members (“protected health information” or “PHI”) is subject to state and federal statutory and regulatory privacy standards, including, without limitation, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (“HIPAA”), the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (the “HITECH ACT”), and regulations adopted thereunder by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 45 C.F.R. Parts 160, 162, 164 (“the HIPAA Rules”).
Provider must establish a program to effectuate full compliance with all applicable state and federal privacy and breach notification laws including, without limitation, HIPAA, 45 CFR §§ 164.400-414 (the “HIPAA Breach Notification Rule,”) and HITECH for the protection of PHI and PII, and for the notification of individuals, appropriate official bodies, and the media in the event of a breach of PHI or PII. Moreover, provider must maintain its privacy compliance and breach notification program in accordance with industry best practices.
Member Access to PHI
Members of Highmark products have a right to access (i.e., to review and/or obtain a copy of) their PHI that is contained in a designated record set. Generally, a “designated record set” contains medical and billing records as well as other records that are used to make decisions about our members’ health care benefits. Therefore, each practitioner must have a mechanism in place to provide this access.
Use of Measurement Data
Highmark uses measurement data to manage members’ health care needs through appropriate quality improvement programs such as health, wellness, and disease management programs.
Protection of Information Disclosed to Plan Sponsors or Employers
Highmark, in general, will disclose PHI only to an authorized representative of a self-insured group health plan. However, Highmark may provide summary health and enrollment information, which has been aggregated and de-identified, to fully insured group health plans and plan sponsors.
Robocalls
Highmark Inc. and its affiliated companies do not release information to artificial intelligence agencies. We will be glad to provide the information needed to the appropriate human stakeholders. Please have a human use our self-service tools available at highmark.com, through our provider portal, or call Customer Service for any information needed.
The Privacy Department
Highmark’s Privacy Department reviews and approves policies regarding the handling of PHI and other confidential information. Online privacy policy may be viewed at highmark.com. At the bottom of the page, click Privacy.
Highmark fully encourages and supports our network physicians’ efforts to provide advice and counsel and to freely communicate with patients on all medically necessary treatment options available, including medication treatment options, regardless of benefit coverage limitations, that may be appropriate for the member’s condition or disease.
In cases where the care, services, or supplies are needed from a provider who does not participate in Highmark’s networks, authorization must be requested.
Members must make decisions based on a full disclosure of options, including potential insurance coverage. Disclosure is the obligation of the treating provider.
Background
Some managed care plans may include a “gag clause” in their provider contracts that limits a network physician’s ability to provide full counsel and advice to enrollees.
Highmark network contracts for all products do not (and never did) contain such a “gag clause” relating to treatment advice, and, in Pennsylvania, complies with Act 68 requirements prohibiting such clauses.
Highmark fully encourages and supports our network physicians’ efforts to provide advice and counsel, and to freely communicate on all medically viable treatment options available, including medication treatment options, which may be appropriate for the member’s condition or disease regardless of benefit coverage limitations. Therefore, we do not penalize and have never penalized physicians for discussing medically appropriate care with the member.
Accessibility Expectations for Providers
To stay healthy, members must be able to see their physicians when needed. To support this goal, we are sharing with you Highmark’s expectations for accessibility of primary care physicians (PCPs), medical specialists, behavioral health specialists, and obstetricians. The standards set forth specific time frames in which network providers should respond to member needs based on symptoms.
Physicians are encouraged to see patients with scheduled appointments within 15 minutes of their scheduled appointment time. A reasonable attempt should be made to notify patients of delays.
Note: Standards for Highmark Healthy Kids (CHIP) enrollees are available in Chapter 2 Unit 3: Other Government Programs and may differ from the expectations noted below.
|
PCP And Medical Specialist Expectations |
|
|---|---|
|
Patient’s Need: |
Performance Standard: |
|
Emergency/life threatening care
|
|
|
Urgent care appointments
|
|
|
Non-urgent, regular care appointments
|
|
|
Routine care appointments
|
|
|
Follow-up visit
|
|
|
After-hours care
|
|
|
In-office waiting times
|
|
|
Maternity Care Expectations (Obstetrics) |
|
|---|---|
|
Patient’s Need: |
Performance Standard: |
|
Maternity Emergency |
|
|
Maternity 1st Trimester |
|
|
Maternity 2nd Trimester |
|
|
Maternity 3rd Trimester |
|
|
Maternity High Risk |
|
|
Behavioral Health Specialist Expectations |
|
|---|---|
|
Patient’s Need: |
Performance Standard: |
|
Care for a life-threatening emergency
|
|
|
Care for a non-life-threatening emergency
|
|
|
Urgent Care
|
|
|
Non-urgent office visit
|
|
|
Routine office visit
|
|
|
After-hours care
|
|
|
In-office waiting times
|
|
Acceptable After-Hours Methods
The chart below outlines acceptable methods of handling after-hours calls from your Highmark patients.
|
Answering Process |
Response/Message |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
Answering Service or Hospital Used as an Answering Service |
Caller transferred directly to provider or clinical staff person covering for the provider |
|
|
Service pages the provider on call (see comment to right) |
A provider or clinical staff person is expected to return the call within 30 minutes |
|
|
Answering Machine |
Message must provide the caller with a way to reach the provider on call by telephone (land line or cell phone) or pager |
Provide clear instructions on how to record a message on a pager (i.e., “you will hear a series of beeps, please enter your phone number, including area code, by pressing the number keys on your phone, then hang up”). A provider or clinical staff person is expected to return the call within 30 minutes. |
|
Instruct caller to leave a message (see comment to right) |
A provider or clinical staff person is expected to return the call within 30 minutes |
Availability of Facility Services
Facility services need to be available to Highmark members on a 24 hour per day, 7 day per week basis when medically appropriate and in accordance with industry standards.
Access to physician services is an integral component of the facility services provided to members. Physician services are provided by either hospital-based physicians or physicians employed by a facility. If physician services are provided to Highmark members on behalf of a facility, the facility must verify that physician has the appropriate training, education, and licensure to provide such services.
Equal Access and Non-Discrimination in Treatment of Members
In addition to requirements contained in your provider agreement and in any other applicable administrative requirements, network providers agree to requirements of equal access and non-discrimination of Highmark members within this manual.
Providers will provide members with equal access at all times to provider services. Providers agree not to discriminate in the treatment of Highmark members, or in the quality of services delivered, on the basis of place of race, national origin, ancestry, religion, sex, including sex stereotypes and gender identity, marital status, sexual preference, disability, age, or the Member’s source of payment, cost, anticipated cost, membership in a Product of Highmark or Health Plan or health status (to include, but not be limited to, medical condition, claims experience, receipt of health care, medical history, genetic information, evidence of insurability, conditions arising out of acts of domestic violence, or disability), or source of payment. Further, providers shall not deny, limit, discriminate or condition the furnishing of provider services to members based on their known or believed relationship or association with an individual or individuals of a particular race, color, national origin, sex, age, or disability.
Communications Access for Individuals with Hearing, Visual, or Speech Impairments
According to the U.S. Department of Justice’s Civil Rights Division (the “DOJ”), a “public accommodation” such as a physician’s office must provide auxiliary aids and services when necessary to ensure that the practice is communicating effectively with individuals with disabilities, unless providing such an aid or service would pose an undue hardship on the practice or fundamentally alter the services provided.
For example, according to the DOJ, if a person has a vision, hearing, or other sensory impairment and that impairment substantially limits the patient’s ability to communicate, a physician’s office must provide auxiliary aids or services to ensure equal access to medical care. The impairment can be one that the patient has from birth or one that has recently developed.
The type of auxiliary aid or service that must be provided will vary according to the length and complexity of the expected communication involved and the nature of the patient’s condition. Treating a hearing impaired patient for a simple cold or the flu may not require a physician’s office to hire a sign language interpreter. Exchanging written notes, typing back and forth on a computer, or using a family member to convey information may be effective.
On the other hand, discussing a complicated diagnosis or answering questions about a planned surgical procedure may require the use of a professional sign language interpreter. Similarly, practices may need to be prepared to have a telecommunication (TDD) device available to communicate effectively with deaf or speech impaired patients and may need to provide large print, audiotapes, or Braille materials for patients with significant sight impairments.
According to the DOJ, a practice may not charge a patient for the additional cost of providing such communication aids and services. Nor may it charge a patient directly for the cost of making the practice’s policies, practices, or procedures ADA-compliant. A health care provider is expected to treat the costs of providing auxiliary aids and services as part of the overhead costs of operating a business.
Administrative Services That Are Permissible to Bill
Providers may collect fair and reasonable fees as permitted by law for providing the following administrative services:
- Completion of forms related to any of the following: employment, driver’s license, and school physicals.
- Providing copies of medical records for the member’s own personal use.
Note: The fees for completion of forms and the provision of copies are permissible when communicated to members in writing prior to requesting payment. In Pennsylvania, the limits on copying charges are updated annually based on the consumer price index and published in the Pennsylvania Bulletin.
Cancellation Fee Assessments
Highmark members are encouraged to keep scheduled appointments or to give adequate notice of delay or cancellation. This is communicated to commercial members in Delaware and to Medicare Advantage members in Pennsylvania as a member responsibility (see Chapter 1 Unit 5: Member Rights and Responsibilities).
Providers may collect a reasonable fee from Highmark members as permitted by law for missed appointments or for cancelling less than 24 hours before a scheduled appointment. If your office policy is to charge for missed appointments or untimely cancellations, this is acceptable as long as the policy is applicable to and enforced with all patients regardless of their payment method or insurance carrier. Members should be advised of the policy upfront prior to any services being rendered or fees assessed.
Providers Cannot Bill for These Services
Below please find common examples of when it is not appropriate to bill Highmark or its members for services. The information below is not an all-inclusive list.
|
Providers Cannot Bill Highmark Members For These Services |
Providers Cannot Bill Highmark For These Services |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The After-Hours Physician Accessibility Study is one of the methods by which physicians are evaluated to determine whether they meet accessibility standards.
Each practice meeting the following requirements participates in the after-hours study:
- New practice sites that have joined the network.
- An annual sample of existing practice site locations.
- Any practice site for which a member complaint (relating to after-hours access) has been received.
- Any provider who appeals a credentialing termination decision based on lack of 24/7 coverage.
The table below describes the process for the after-hours accessibility study:
|
Step |
Action |
|---|---|
|
1 |
A Highmark representative calls the practice’s main telephone number after normal practice hours. |
|
2 |
The Highmark representative verifies that the practice has an acceptable after hours process in place to respond to patient calls after regular business hours. Does the physician have an acceptable process?
|
|
3 |
A letter is sent to the office informing the provider of the results and the requirements for after hours accessibility (answering service, provider is paged, etc). Highmark will call the provider’s office after regular business hours two weeks after the letter is sent to the provider to determine if the office has implemented corrective actions. |
Practices that remain non-compliant following Step 3 of the process may be subject to additional corrective action, sanctioning, and, ultimately, network termination.
The following entities, which serve the noted regions, are independent licensees of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association: Western and Northeastern PA: Highmark Inc. d/b/a Highmark Blue Cross Blue Shield, Highmark Choice Company, Highmark Health Insurance Company, Highmark Coverage Advantage Inc., Highmark Benefits Group Inc., First Priority Health, First Priority Life, Highmark Care Benefits Inc., or Highmark Senior Health Company. Central and Southeastern PA: Highmark Inc. d/b/a Highmark Blue Shield, Highmark Benefits Group Inc., Highmark Health Insurance Company, Highmark Choice Company or Highmark Senior Health Company. Delaware: Highmark BCBSD Inc. d/b/a Highmark Blue Cross Blue Shield. West Virginia: Highmark West Virginia Inc. d/b/a Highmark Blue Cross Blue Shield, Highmark Health Insurance Company or Highmark Senior Solutions Company. Western NY: Highmark Western and Northeastern New York Inc. d/b/a Highmark Blue Cross Blue Shield. Northeastern NY: Highmark Western and Northeastern New York Inc. d/b/a Highmark Blue Shield.
All references to “Highmark” in this document are references to the Highmark company that is providing the member’s health benefits or health benefit administration and/or to one or more of its affiliated Blue companies.
All revisions to this Highmark Provider Manual (the “manual” or “Highmark Provider Manual”) are controlled electronically. All paper copies and screen prints are considered uncontrolled and should not be relied upon for any purpose.